Explain Differences in Solubility Based on Imfs
It is important to consider the solvent as a reaction parameter. IMFs are the various forces of attraction that may exist.
Solved Differences In Solubility Can Be Explained By Chegg Com
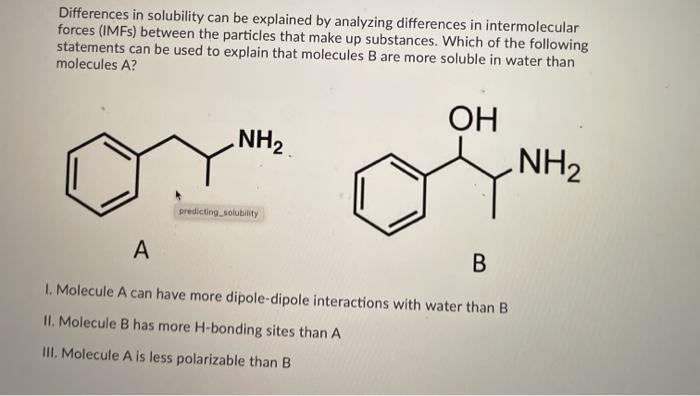
Differences in solubility can be explained by analyzing differences in intermolecular forces IMFs between the particles that make up substances.
. Solutions of hydrogen in palladium may be formed by exposing Pd metal to H2 gas. But that is strong enough to make molecules stick to each other and form condensed phases. LUUSIVU UITPURI Differences in solubility can be explained by analyzing differences in intermolecular forces IMFs between the particles that make up substances.
The first force London dispersion is also the weakest. Molecule B is less polar than A II. The type of intermolecular forces IMFs exhibited by compounds can be used to predict whether two different compounds can be mixed to form a homogeneous solution soluble or miscible.
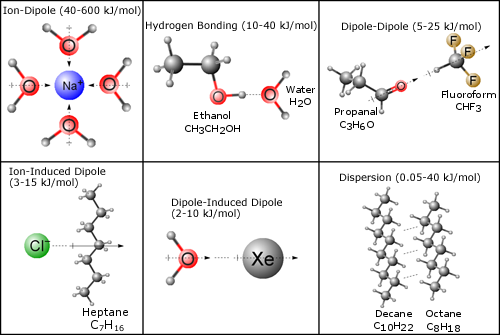
Figure of intermolecular attraction between two H-Cl molecules and intramolecular attraction within H-Cl molecule. A saturated solution is a solution where a given amount of solute is completely soluble in a solvent at a given temperature. Intermolecular forces are forces that exist between molecules.
Molecule and solvent molecule the greater the solubility of the solute in the solvent. Increased surface area more surface exposed rate increases. 2 Jul 5 2018.
Based on solubility different types of solution can be obtained. It has weaker intermolecular forces than water so because of this hydrogen. Intermolecular forces often abbreviated to IMF are the attractive and repulsive forces that arise between the molecules of a substance.
1Identify the major types of IMFs in solutions and their relative strengths. SA by crushing or stirring. Vapor Pressure and Temperature 0C 40C Water 061 737 Ethanol.
Which of the following statements can be used to explain that molecules B are more soluble in water than molecules A. In London dispersion the intermolecular attraction. IMFs are much much weaker than chemical bonds - about 10 weaker.
Feb 14 2020 So vapour pressure of a liquid acetone is higher than the water in a closed. Develop a law that will allow you to predict the solubility of a substance in water or hexane and then develop an. Solution without h20 as the solvent.
The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces IMFs and the kinetic energies KE of its molecules. The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces IMFs and the kinetic energies KE of its molecules. Forms of attraction form dissociation hydration ions kept separate by h20 How can increasing the surface area affect the rate of solution.
Coulombs law is still in effect but the forces are much weaker now. Which of the following statements can be used to explain that molecules B are more soluble in water than molecules A. Intramolecular forces are the forces that hold atoms together within a molecule.
Intermolecular forces are responsible for most of the physical and chemical properties of matter. Substances that exhibit hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole forces are generally water soluble whereas those that exhibit only London dispersion forces are generally insoluble. Apply the likes dissolves likes rule with identity of IMFs to determine if two substance will form a solution.
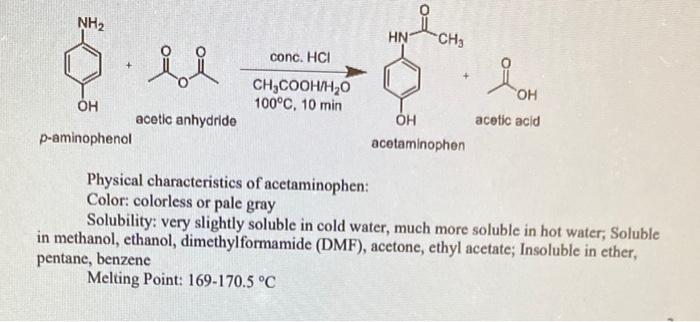
NH2 OH NH2 A B 1. The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces IMFs and the kinetic energies KE of its molecules. Arrange the following in order of increasing boiling point.
IMFs are the various. Polar molecules are soluble in polar solvents Predominant intermolecular force is dipole-dipole attraction between polar solute molecule and polar solvent molecule. Nonpolar molecules are soluble in nonpolar solvents Predominant intermolecular.
Solubility Demonstration Consider the intermolecular forces in water H 2O hexane C 6H 14 potassium permanganate KMnO 4 iodine I 2 Instructional Objectives 1. Molecule A can have more dipole-dipole. Stronger IMF Higher enthalpy of vaporization ΔH vap takes more energy at constant atmospheric pressure to turn liquid to gas Stronger IMF Higher viscosity a thicker liquid flows more like molasses Stronger IMF Higher surface tension more resistant to deformation from poking Truong-Son N.
Be able to predict solubility based on the intermolecular forces of the components. IMFs are the various forces of attraction that may exist. Understand the solubility of non-reactive gases.
These forces mediate the interactions between individual molecules of a substance. Identify the major types of IMFs in solutions and their relative strengths. This demo is usually performed when discussing the formation of solutions involving intermolecular forces and solubility.
On the other hand a supersaturated solution is those where solute starts salting out or precipitate after a particular concentration is dissolved at the. Heat is absorbed when the total IMFs in the solution are weaker than the total of those in the pure solute and in the pure solvent. Explore the solubility differences of the different solutes below in hexane and water.
The differences in the properties of a solid liquid or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms molecules or ions that make up each phase. Explain how an ionic solute dissolves in water. Another polar molecules is ammonia NH_3 whose trigonal pyrimidal shape and electronegativity different in N-H bonds of 09 make this substance soluble in water.
You might expect they might dissolve different types of solutes. The differences in the properties of a solid liquid or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms molecules or ions that make up each phase. In water the electronegativity difference between oxygen 35 and hydrogen21 is 14 35-2114.
All three of these forces are different due to of the types of bonds they form and their various bond strengths. And explain the differences in their room-temperature phases. The differences in the properties of a solid liquid or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms molecules or ions that make up each phase.
The water solubility of molecular compounds is variable and depends primarily on the type of intermolecular forces involved. Because organic chemistry can perform reactions in non-aqueous solutions using organic solvents. NH2 OH NH2 predicting_colubility A B I.
There are three intermolecular forces of ethanol. Apply the likes dissolves likes rule with identity of IMFs to determine. Breaking stronger IMFs and forming weaker IMFs absorbs heat.
This and waters bent shape make water a polar molecule. They are London dispersion dipole-dipole and the hydrogen bond.

Solved In Your Own Words Define A Solution A Mixture That Containing Of A Solvent And One Or More Solutes Explain Why Imfs Are Responsible For Changes Of Solubility Of The Same Substance
Solutions And Attractive Forces
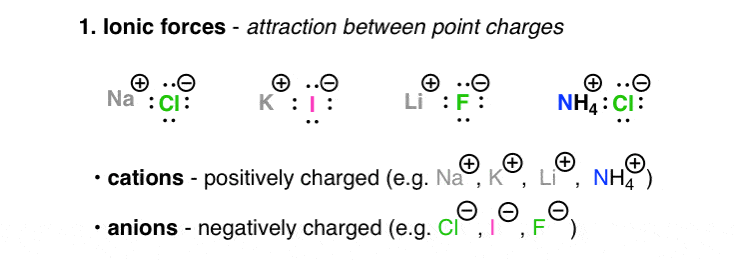
The Four Intermolecular Forces And How They Affect Boiling Points

4 4 Solubility And Intermolecular Forces Sl Youtube
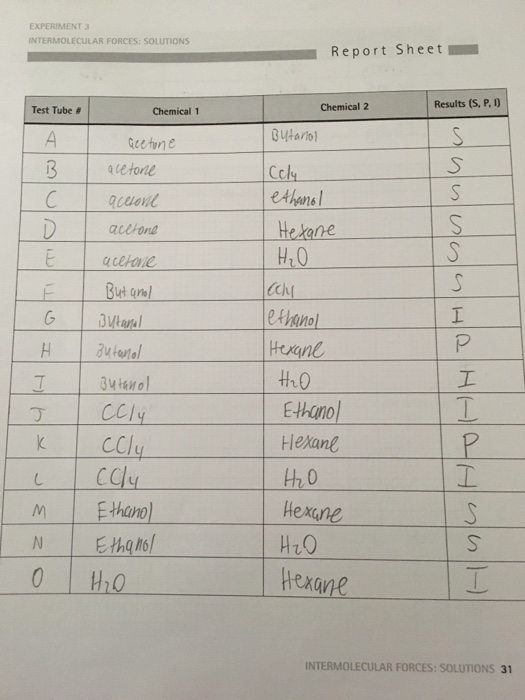
Solved 2 In Lab 2 You Will Be Testing The Solubility Of Chegg Com

Newburyport High School Unit 3 Intermolecular Forces Properties
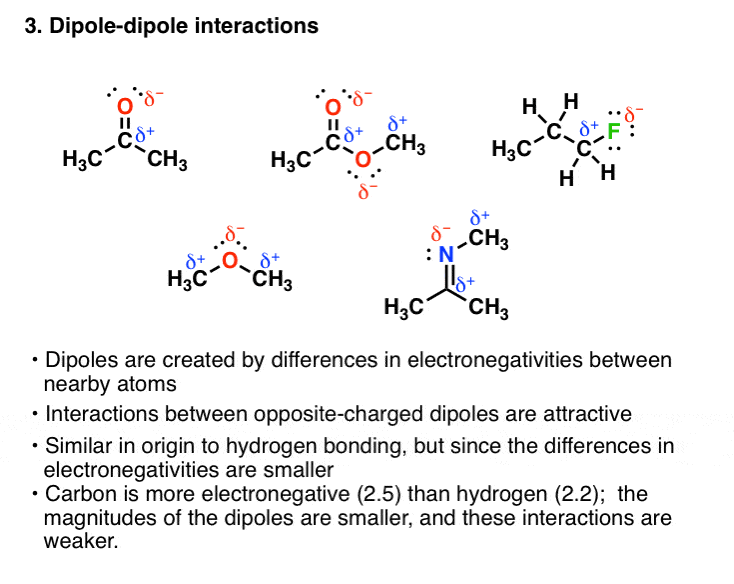
The Four Intermolecular Forces And How They Affect Boiling Points
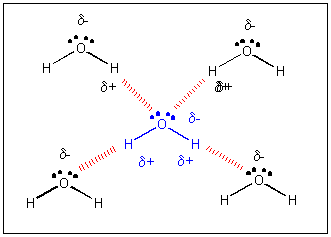
Intermolecular Forces And Solutions

Solved Explain Your Results In Terms Of Imfs For The Chegg Com

Solved Explain Your Results In Terms Of Imfs For The Chegg Com
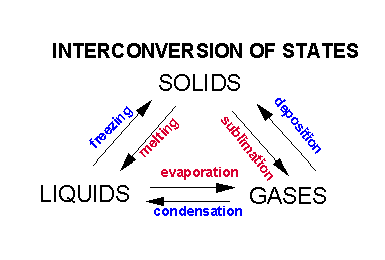
Intermolecular Forces And Solutions
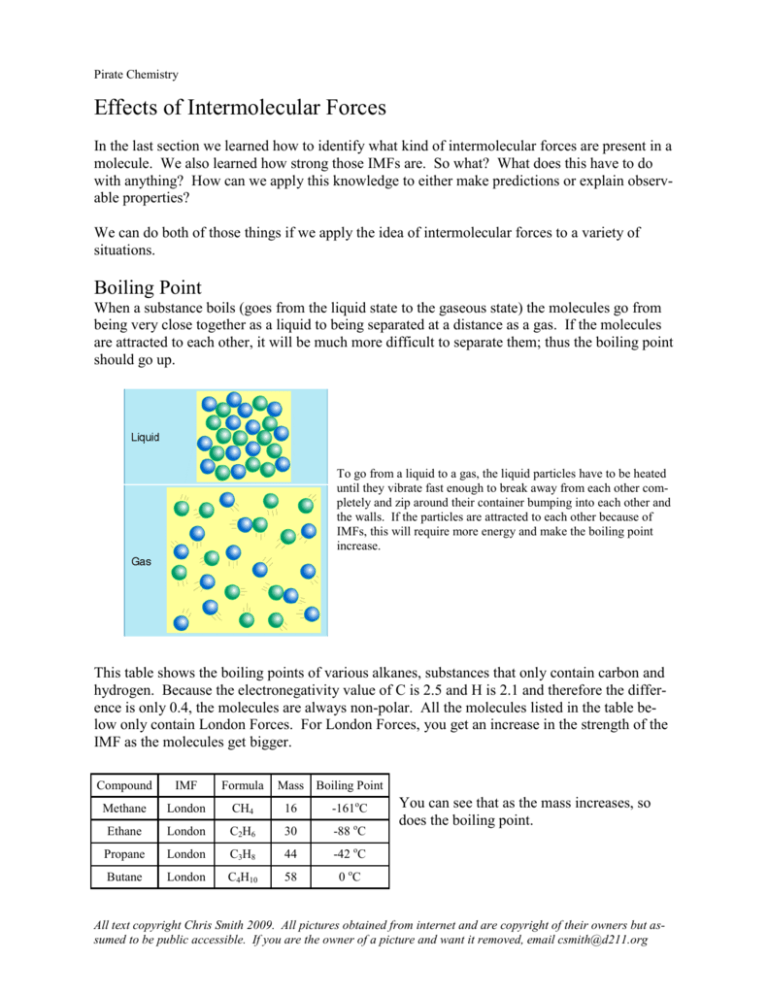
6 Effects Of Intermolecular Forces
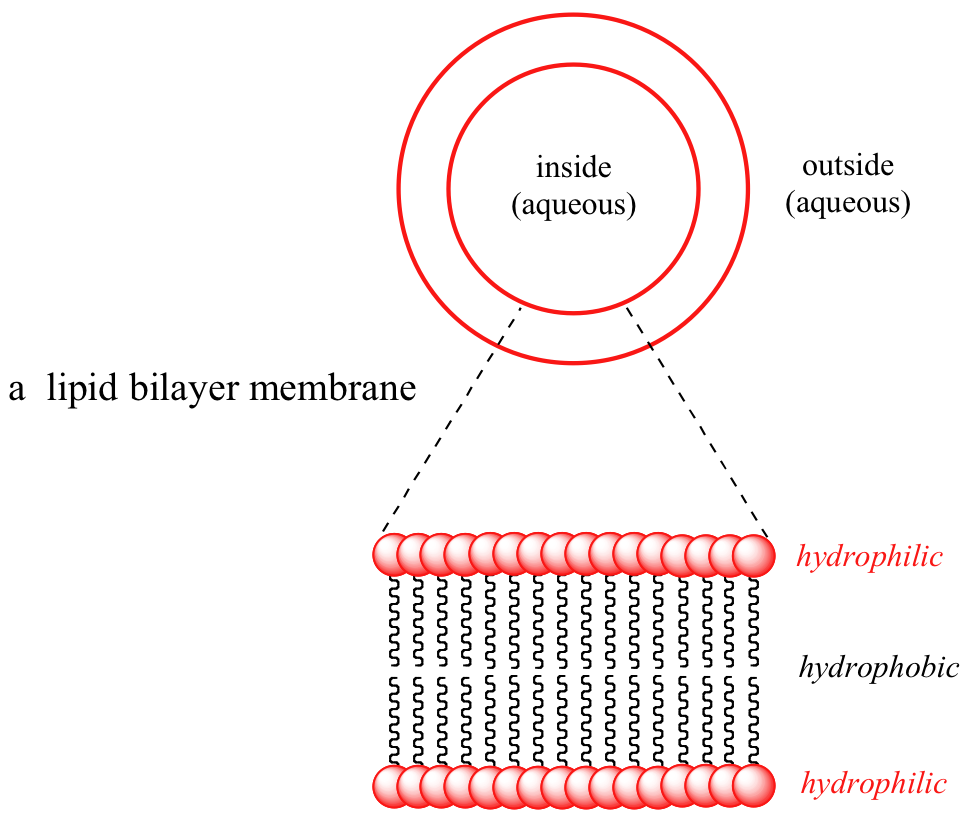
2 12 Intermolecular Forces And Solubilities Chemistry Libretexts
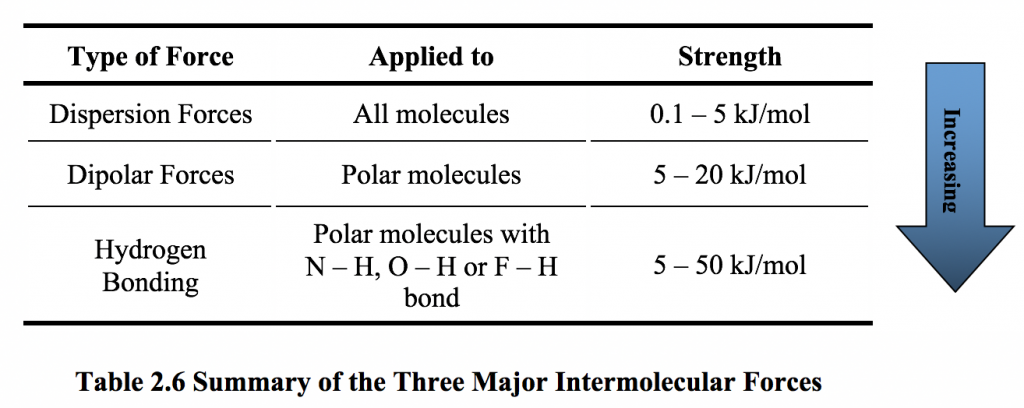
2 6 Intermolecular Force And Physical Properties Of Organic Compounds Chemistry Libretexts
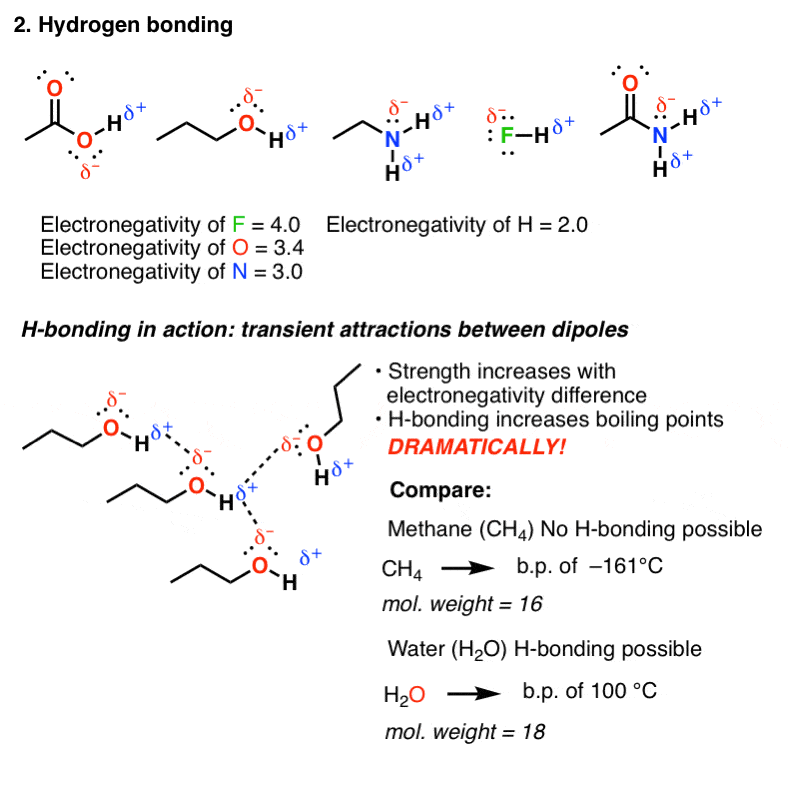
The Four Intermolecular Forces And How They Affect Boiling Points
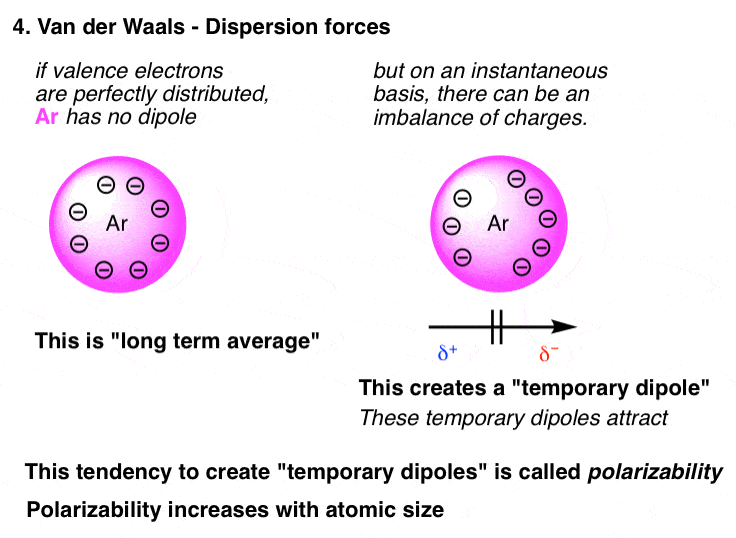
The Four Intermolecular Forces And How They Affect Boiling Points
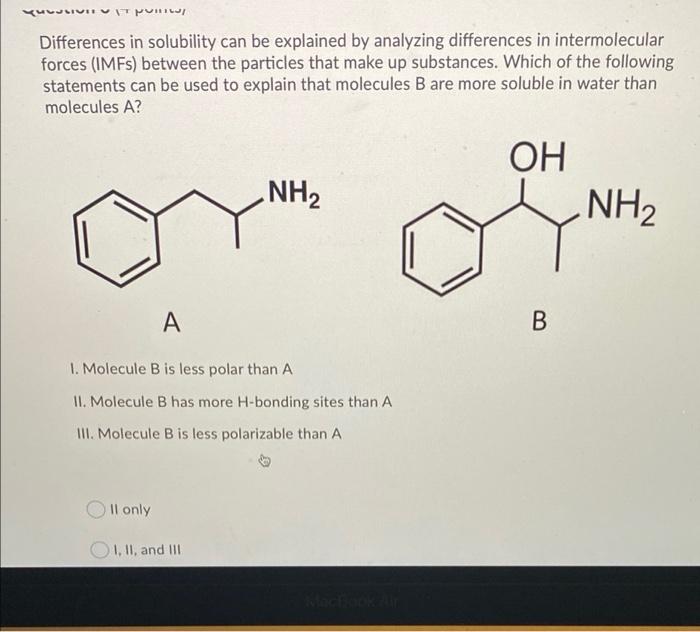
Solved Luusivu Uitpuri Differences In Solubility Can Be Chegg Com


Comments
Post a Comment